Tech Features
The Role of Edge Computing and Spatial Data in Urban Development in the Middle East

Dr. Fadi Alhaddadin, Assistant Professor, Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Heriot-Watt University Dubai.
As urbanisation accelerates in the Middle East, cities are evolving into hubs of innovation to address population growth, manage limited resources, and enhance quality of life. Smart cities are central to the region’s digital transformation, with the integration of spatial data and edge computing revolutionising urban planning. These technologies allow for distributed data processing at the network’s edge, reshaping the management of infrastructure, resources, and citizens. In this article, Dr. Fadi Alhaddadin explores the impact of edge computing and spatial data on the transformation of Middle Eastern cities, offering recent statistics and regional examples.
The Rise of Smart Cities in the Middle East
The smart city concept appeals to many countries in the Middle East as they work towards a better future reliant on technological innovations. Nations such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia have taken a leading role in these strategies by applying modern technologies in their cities’ administration, providing services, and maintaining living conditions.
This transformation has been accelerated by a key factor: edge computing. Edge computing refers to a computing architecture that processes data at its source, rather than relying exclusively on centralised cloud systems. By minimising latency and improving the quality of real-time outcomes, edge computing meets the demands of smart cities. It enables the integration of spatial data—information about the location of objects or events—into urban planning, infrastructure development, and the provision of public services.
Augmenting Infrastructure through Edge Computing
Infrastructure forms the foundation of any smart initiative, and the Middle East is increasingly leveraging edge computing to optimise the management of its critical systems. For roads, bridges, water, and energy grids, edge computing enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency.
In Dubai, as part of the Smart Dubai program, edge computing has been integrated into the city’s urban infrastructure to manage traffic and promote public transport use. Sensors and IoT devices across the city enable real-time data collection, allowing traffic control systems to adjust signals, re-route vehicles, and swiftly reduce delays.
Moreover, NEOM, a smart city under construction in Saudi Arabia, is utilising edge computing to manage its transportation networks, nuclear facilities, and renewable energy grids. With a focus on real-time data analysis, NEOM aims to reduce energy consumption and create a fully sustainable urban ecosystem. Projections suggest that by 2030, this smart city could contribute up to $48 billion to Saudi Arabia’s GDP, showcasing the economic potential of embracing advanced technologies.
Optimising Resource Management
The third crucial aspect of urbanisation is efficient resource management, which, in the Middle East, largely involves handling limited natural resources like water and energy. The integration of edge computing and spatial data presents significant opportunities to optimise the use of these essential resources.
Adopting these technologies also supports the growth of the region’s renewable energy sector. Masdar City in the UAE, recognised as one of the world’s most sustainable urban areas, utilises edge computing to monitor and manage its solar power systems. By applying geospatial data on solar irradiance and weather conditions, Masdar City ensures its solar panels operate at peak efficiency. This reliance on renewable energy has enabled the city to reduce its dependence on conventional energy sources, with most of its power coming from sustainable resources.
Enhancing Citizen Engagement
One notable impact of smart city technologies is the improvement of citizen engagement. By leveraging edge computing to integrate spatial data, cities can better tailor their services to meet residents’ needs, enhancing overall efficiency. This fosters active participation and greater satisfaction among citizens, who can play a role in managing the urban environment.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the integration of edge computing and spatial data holds significant potential, it also presents certain challenges. The primary concern is data security and privacy, as the increased generation of data at the network’s edge raises the risk of cyber threats. To ensure the success of smart cities, robust cybersecurity measures must be put in place to safeguard the core systems.
Additionally, these technologies often require substantial investment in infrastructure, such as 5G networks and IoT devices. Achieving scalability and sustainability in smart city initiatives would demand collaboration between government and private sector stakeholders.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities far outweigh the risks. With the growing adoption of edge computing and spatial data, Middle Eastern cities are well-positioned to develop sustainable, resilient urban centers that prioritise citizens while driving economic growth.
Conclusion
The integration of edge computing and spatial data is fundamental to the Middle East’s vision for smart cities. These technologies are reshaping urban environments by improving infrastructure, optimising resource management, and boosting citizen engagement. Cities such as Abu Dhabi, Dubai, and Riyadh are leading the way, demonstrating how technology can create smarter, greener cities for the future. Although this transformation is still in its early stages, the region has the potential to become a trailblazer in the smart city revolution.
Tech Features
HOW WOMEN SCIENTISTS CAN ACCELERATE NATIONAL INNOVATION GOALS
Dr Heba El-Shimy, Assistant Professor (Data and AI), Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Heriot-Watt University Dubai

Healthy societies, institutions, or teams operate best when comprising a healthy balance between males and females. A landmark study by Boston Consulting Group (BCG) with the Technical University of Munich uncovered that companies with above-average gender diversity generated around 45% of their revenues from innovative products, compared to only 26% as innovative revenues for companies with below-average gender diversity. These findings are echoed in the scientific field. A 2025 study by Nature analyzing 3.7 million US patents revealed that inventing teams with higher participation of women are associated with increased novelty in patents. Research by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology confirms that teams with more women exhibit significantly higher collective intelligence and are more effective at solving difficult problems. These studies tell one clear story: that participation of women in innovative and scientific fields is not only desirable — it is a strategic national asset.
UAE Women In STEM
The UAE holds one of the world’s most striking gender profiles in STEM education. According to UNESCO data, 61% of graduates in STEM fields are Emirati women, surpassing the Arab world average of 57% and nearly doubling the global average of 35%. At government universities, 56% of graduates are women, and they represent over 80% of graduates in natural sciences, mathematics, and statistics.
These numbers have translated into accomplishments that have captured global attention. The Emirates Mars Mission — the Hope Probe — was developed by a team of scientists that was 80% women, selected based on merit. Noora Al Matrooshi became the first Arab woman to complete NASA astronaut training in 2024. The Chair of the UAE Space Agency and the mission’s Deputy Project Manager is a woman: H.E. Sarah Al Amiri. At Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI), female enrolment reached 28% within five years and continues to grow. Women’s talents are being recognised — this is not a mere future ambition, but a present reality.
Scientific Research As An Engine For National Strategy
The ‘We the UAE 2031’ vision sets ambitious goals: doubling GDP to AED 3 trillion, generating AED 800 billion in non-oil exports, and positioning the country as a global hub for innovation, artificial intelligence, and entrepreneurship. The UAE’s rise to the 30th place in WIPO Global Innovation Index 2025 signals a steady pace towards achieving the UAE 2031 vision. Sustaining this ascent requires continued investment into human capital to produce research output, intellectual property, and commercial innovation at a pace matching the ambition. This is precisely where women scientists become indispensable.
Women scientists are already major contributors to the seven priority sectors identified in the UAE National Innovation Strategy: renewable energy, transport, education, health, technology, water, and space. UAE women scientists are research-active in climate science, sustainable materials, clean energy systems, AI-driven diagnostics in healthcare, and environmental monitoring — all crucial sciences that the national development commitments depend on.
Knowledge economies are built on the ability to generate, apply, and commercialize research locally — reducing the dependence on imported technologies and creating self-sustaining innovation ecosystems. When a researcher at UAEU develops patented computational methods for drug design, as Dr. Alya Arabi recently did with four patents spanning AI-driven pharmaceutical development and medical devices, that is intellectual property created on UAE soil, addressing healthcare challenges that would otherwise require imported solutions. When women scientists at Masdar City and Khalifa University advance research in solar energy systems, carbon captured materials, or sustainable desalination, they are producing foundational science that the UAE’s Net-Zero 2050 Strategy depends upon.
Masdar’s WiSER (Women in Sustainability, Environment and Renewable Energy) programme has graduated professional young women from over 30 nationalities, closing the gap in the global sustainability workforce. In healthcare, women scientists are active in the areas where AI, genomics, and precision medicine converge. The Emirati Genome Programme, M42’s Omics Center of Excellence, and the Abu Dhabi Stem Cells Center all represent domains where locally produced research can reduce the country’s reliance on imported diagnostics and therapeutics.
From these examples, it is clear that women scientists’ and researchers’ contributions are a central pillar of the national R&D ecosystem.
A Regional And Global Perspective
The UAE’s experience is instructive for the wider region. Across the Arab world, up to 57% of STEM graduates are women, yet the MENA region maintains one of the lowest female workforce participation rates globally at 19%. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 has made notable progress, with women’s workforce participation reaching 36.2% and women now comprising 40.9% of the Kingdom’s researchers. The challenge across the GCC and MENA is consistent: converting educational attainment into sustained professional participation and research output. Globally, only one in three researchers is a woman, and parity in engineering, mathematics, and computer science is not projected until 2052. UNESCO’s 2026 International Day of Women and Girls in Science theme — “From Vision to Impact” — captures this urgency well.
The Way Forward: From Vision To Impact
As an academic working at the intersection of artificial intelligence and healthcare research in Dubai, I witness this potential daily — in students who arrive with rigour and ambition, in researchers producing work that stands alongside the best globally, and in a national ecosystem that increasingly treats women’s scientific participation as a strategic priority rather than a social courtesy. But policies alone do not produce innovation. What produces innovation is funding, access to facilities, clear pathways from research to commercialisation, and the recognition that a woman scientist publishing a patent in the UAE is building national capability in exactly the same way as the infrastructure projects that make headlines.
Sustained commitment is key — from governments, institutions, and the private sector — to ensure that every woman scientist in this region has the funding, the platforms, and the pathways to convert her research into national impact. When women scientists thrive, nations innovate faster. The UAE understands this. Now it must ensure the rest of the ecosystem does too.
Tech Features
WOMEN IN AI AND DATA SCIENCE: WHO IS BUILDING THE ALGORITHMS THAT SHAPE OUR FUTURE?
Dr Maheen Hasib, Global Programme Director for BSc Data Sciences, School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Heriot-Watt University Dubai

Artificial intelligence (AI) and data science are no longer distant or experimental ideas. They quietly sit behind many of the decisions that shape our everyday lives: how patients are diagnosed, how job applications are filtered, how loans are approved etc. These systems increasingly influence who gets opportunities and who does not. That reality makes one question impossible to ignore: who is building the algorithms that shape our future?
As a Programme Director for the Data Sciences programme at Heriot-Watt University, this question is not just academic for me, it is deeply personal. Every year, I meet capable, curious, and motivated young women who are genuinely interested in data science. Yet many hesitate. Not because they lack ability, but because they are unsure whether they truly belong in the field. Too often, they do not see people (like themselves) reflected in AI research, technical teams, or leadership roles. And that absence matters.
When bias in AI feels uncomfortably familiar
AI systems are often described as objective or neutral, yet they are trained in data shaped by human history, something that is far from neutral. When training data reflects existing gender imbalances, AI systems can replicate and even magnify those patterns. This has led to technologies that perform less accurately for women, fail to capture women’s health needs, or disadvantage women in recruitment and evaluation processes.
For many women, these outcomes feel uncomfortably familiar. They echo everyday experiences of being overlooked, misunderstood, or underrepresented. In most cases, this is not the result of deliberate exclusion. It is the consequence of design choices made without diverse perspectives at the table.
Why representation goes beyond numbers
Representation in AI and data science is often discussed in terms of statistics or diversity targets. But at its core, representation is about perspective. When women are involved in developing AI systems, they help shape how problems are defined, what data are considered relevant, and which risks are taken seriously.
From an academic perspective, diverse teams produce more robust research and better-tested models. From a human perspective, they help ensure that AI systems work for the full range of people they are meant to serve. Inclusion improves both technical quality and social impact, it strengthens the science and the society it serves.
Women and the future of ethical AI
Many women working in AI are already at the forefront of discussions around fairness, transparency, explainability, and responsible data use. These are not peripheral concerns; they are central to building trustworthy AI. Ethical AI requires asking difficult questions: Who might be harmed when a system fails? Whose data is missing? Who is affected by design decisions that seem minor on the surface?
By advocating for human-centered approaches, women in AI are helping shift the field beyond purely performance-driven metrics toward systems that balance innovation with responsibility.
Education, encouragement, and visibility matter
At Heriot-Watt University Dubai, we make a deliberate effort to encourage women to pursue data science, not just as a degree, but as a long-term career. This means creating supportive learning environments, highlighting female role models, and openly discussing the wide range of paths that data science can lead to. Students need to see that success in AI does not follow a single template.
Equally important are spaces where women can connect, share experiences, and feel supported. As an ambassador for Women in Data Science, I have seen how such events play a vital role. They create visibility, build confidence, and remind women that they are not alone. We need more of these initiatives, not as one-off celebrations, but as sustained platforms for mentorship, networking, and growth.
Encouraging women in AI is not about lowering standards or meeting quotas. It is about recognizing that inclusive participation leads to better research, more ethical technologies, and systems that genuinely reflect the societies they shape.
Conclusion
As AI and data science continue to influence our world, we must ask not only what these systems do, but who designs them. Supporting women to study data science, pursue AI careers, and step into leadership roles is essential to building technologies that are fair, responsible, and trustworthy. Through education, visibility, and initiatives, we can help ensure that the future of AI is shaped by many voices.
The future of AI should be one where women do not simply use technology but actively shape it.
Tech Features
INSIDE THE TECHNOLOGY THAT MAKES HUAWEI FREECLIP THE BEST OPEN-EAR EARBUDS!
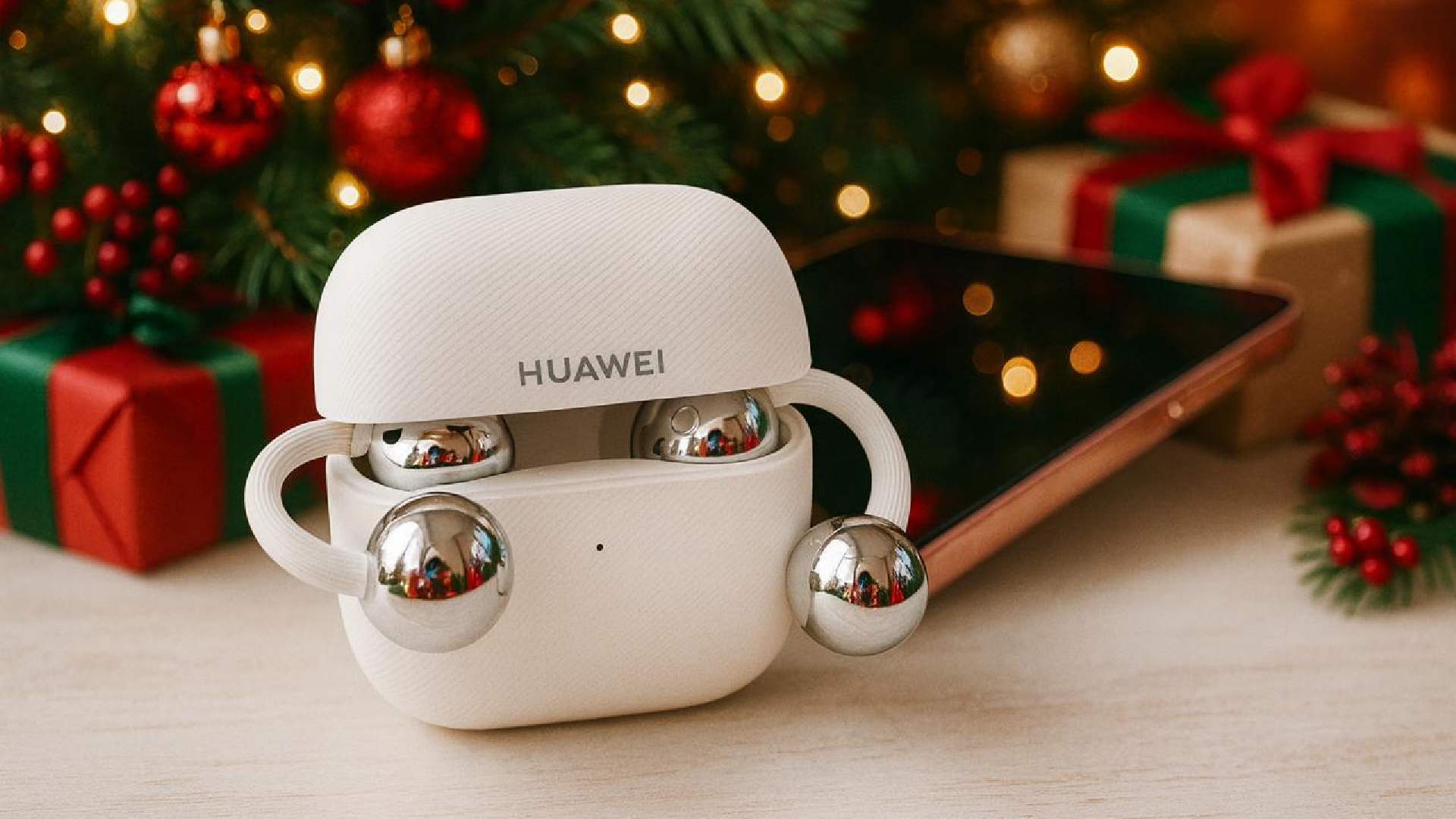

It has been two years since the debut of the original HUAWEI FreeClip, Huawei’s first-ever open earbuds that took the market by storm. Its massive popularity proved that the world was ready for a new kind of listening experience. The new HUAWEI FreeClip 2 tackles the hard challenges of open-ear acoustics physics head-on, combining a powerful dual-diaphragm driver with computational audio. It delivers depth and clarity, which was once thought impossible with an open-ear design.
Solving the acoustic limitations of open-ear audio alone would have been sufficient to make the HUAWEI FreeClip 2 our pick for best open-ear audio. But it is way more than that.
Comfortable C-Bridge design
The HUAWEI FreeClip 2 earbuds weigh only 5.1 g per bud, a 9% reduction from the previous generation. This lightweight architecture ensures an effortless experience, perfect for long calls, workouts, and commutes, allowing you to wear them all day without fatigue. The comfort bean is 11% smaller than the previous model, yet the design provides a secure fit that prevents the earbuds from falling out, even during intense activity.
Constructed from a new skin-friendly liquid silicone and a shape-memory alloy, the C-bridge is 25% softer and significantly more flexible than its predecessor. Finished with a fine, textured surface, it ensures a comfortable, irritation-free wearing even after extended use.
Adaptive open-ear listening
The acoustic system has been significantly upgraded, featuring a dual-diaphragm driver and a multi-mic call noise cancellation system. This setup not only delivers powerful sound but also maximises space efficiency. That’s why, despite their small size, these earbuds can deliver substantial acoustic performance.
The Open-fit design of the earbuds demands high computing power to maintain sound quality and call clarity. The HUAWEI FreeClip 2 offers ten times the processing power of the previous generation, serving as Huawei’s first earbuds to feature an NPU AI processor for a truly adaptive experience. The new dual-diaphragm driver includes a single dynamic driver with two diaphragms, effectively doubling the sound output within a compact space to provide a significant boost in volume and bass response.
Furthermore, the earbuds dynamically detect surrounding noise and adjust volume and voice levels in real-time. If the environment is too noisy, the system uses adaptive voice enhancement to specifically boost human frequencies, ensuring you never miss a word of a podcast or audiobook. When you return to a quiet environment, the earbuds automatically settle back to a comfortable volume level.
Crystal clear calls
To ensure call quality in chaotic environments, the HUAWEI FreeClip 2 utilises a three-mic system combined with multi-channel DNN (Deep Neural Network) noise cancellation algorithms. This system intelligently identifies and filters out ambient noise. Thanks to the NPU AI processor, the earbuds automatically enhance voice clarity, ensuring your conversations remain crisp regardless of your surroundings.
Battery life and charging
With the charging case, the HUAWEI FreeClip 2 offers a total battery life of 38 hours, allowing users to enjoy music throughout a full week of commuting on a single charge. On their own, the earbuds last for 9 hours—enough for a full workday of uninterrupted calls. For those in a rush, just 10 minutes of fast charging in the case provides up to 3 hours of playback. For added convenience, they support wireless charging and are compatible with watch chargers.
Rated IP57, the earbuds are resistant to sweat and water. They can easily withstand intense workouts or even a downpour.
Connectivity
The earbuds support dual connections and seamless auto-switching across iOS, Android, and Windows. When connected to EMUI devices, you can even switch audio between more than two devices. Additionally, when connected to a PC, the earbuds allow you to answer an incoming call without disconnecting from or interrupting your conference setup.
It is, quite simply, a pair of earphones reliable enough for the gym, the office, and the commute.
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoDenodo Bolsters Executive Team by Hiring Christophe Culine as its Chief Revenue Officer
-
News10 years ago
SENDQUICK (TALARIAX) INTRODUCES SQOOPE – THE BREAKTHROUGH IN MOBILE MESSAGING
-

 VAR11 months ago
VAR11 months agoMicrosoft Launches New Surface Copilot+ PCs for Business
-

 Tech Interviews2 years ago
Tech Interviews2 years agoNavigating the Cybersecurity Landscape in Hybrid Work Environments
-

 Tech News8 months ago
Tech News8 months agoNothing Launches flagship Nothing Phone (3) and Headphone (1) in theme with the Iconic Museum of the Future in Dubai
-

 Automotive1 year ago
Automotive1 year agoAGMC Launches the RIDDARA RD6 High Performance Fully Electric 4×4 Pickup
-

 VAR2 years ago
VAR2 years agoSamsung Galaxy Z Fold6 vs Google Pixel 9 Pro Fold: Clash Of The Folding Phenoms
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBrighton College Abu Dhabi and Brighton College Al Ain Donate 954 IT Devices in Support of ‘Donate Your Own Device’ Campaign