News
Are biometrics the backbone of personal security in smart cities?

By: Alexander Migutsky, Advanced Technologies Specialist, Positive Technologies
Alexandra Murzina, Head of Advanced Technologies Department, Positive Technologies
What makes smart cities so fascinating is the level of personalization the ecosystem promises across essential daily staples including work, transport, payments, and complete control over applications at home.
With immeasurable IoT applications and effective use of big data analytics, smart cities will emerge a phenomenon that seeks to make us question how we ever managed to operate any other way.
Achieving this level of personalization won’t be easy though. A larger interconnected network requires paths to identify users so they can tailor their experiences to themselves. Whether it be biometric ID cards or authentication portals, users should be able to authenticate themselves and connect to networks using their personal information.
Biometrics are widely used in enterprise security, access control, and banking operations, with facial recognition and fingerprint authentication systems now commonplace in companies, subways, stores, and restaurants.
The demand for biometric technologies is being driven, among other things, by the increasing adoption of biometric systems in the automotive and consumer electronics industries.
But are biometrics geared to provide comprehensive support to smart city infrastructure?
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global biometric system market size is projected to reach USD 76.70 billion by 2029.
However, there are still safety concerns about how these systems operate and make decisions; questions arise – Exactly how safe are these systems? How do they work under the hood, how do they make decisions?
Positive Technologies’ in-house team of cybersecurity experts conducted a white hat investigation focusing on physical and cyber threats to machine learning systems, including attacks that aim to compromise system confidentiality and obtain data.
The goal of the investigation was to discover gaps within biometric security systems leading up to their inevitable integration into smart infrastructure. We hope that our findings can shed some much needed light upon how the industry can collectively ensure seamless connectivity and functionality within biometric authentication systems supporting smart infrastructure.
During our investigation, we took apart two biometric devices and examined their internal electronics.
Device 1
The first device is expensive and uses advanced technology with the latest biometric algorithms. It has a depth camera, two conventional cameras, and an IR dot projector. A depth camera uses a combination of technologies to obtain depth information, increasing the reliability of the biometric system, which means attackers would need to know the user’s face geometry and have the ability to recreate it. Naturally, a device with such technology is used in access control systems at airports worldwide. Such a device is bound to be a staple of central transportation hubs in smart cities. So, how reliable is the device really?
During testing, we discovered that the device has liveness detection to identify whether the biometric source is real. The cameras capture the image, which is then received by deep neural networks for processing.
We found vulnerabilities in the system, particularly through remote code execution (RCE) attacks, which allowed us to extract machine learning models and user vectors to recreate the biometric authentication algorithm. We attempted to restore a user’s face from the representation hidden in the database.
Although we had a shot at carrying out a successful attack, there was probably a lot of optical distortion in real conditions, due to which we lost some points.
Security analysis:
- Developers did not use depth camera data for authentication which allowed us to circumvent the authorization algorithm.
- The algorithmic assessment failed when we attempted to generate an artificial face matching a real person’s biometric pattern, but attackers could potentially succeed with more time.
Device 2
The second device we studied was a biometric terminal for tracking employees’ work hours – crucial to supporting enterprise workforces within smart cities. It wasn’t as advanced as the first device as it lacked CUDA cores for complex neural networks. However, it used machine learning algorithms from the 2010s and had two cameras: one conventional and one infrared for biometric authentication.
The infrared camera is the key feature of the terminal. It captures invisible details, making it difficult to trick the system. The terminal uses a cascade classifier, 15 Gabor filters, and an algorithm for local binary patterns in the infrared range to detect and analyze facial features. Although it has some vulnerabilities, such as recognizing the same user with and without glasses as different people, the combination of technologies provides decent defense against attacks.
Security analysis: The biometric terminal is less flexible than the first device because it uses only the infrared range and classic algorithms. Nonetheless, this design makes it more resistant to attacks.
Conclusively
Having studied biometric access control terminals that use different algorithms, we discovered that the terminal with neural networks is flexible and can authenticate users wearing masks, helmets, or makeup, but it can be hacked through considerably antiquated mirroring tactics.
The terminal using classic machine learning algorithms is more resistant to illegal authentication attempts. However, both terminals are vulnerable to remote code execution attacks.
Our recommendations for developers looking to strengthen biometric device security include:
- Using data from the depth sensor to distinguish between individuals.
- Conducting independent device audits.
- Collaborating with security researchers and be open to receiving help.
Developing devices for smart city infrastructure is a complex process that requires experts conducting diligent trial and error routines to ensure frictionless operational capacity across the grid.
Even highly skilled teams can make mistakes, leading to vulnerabilities in the final product. Being open to feedback from real users and experts are key to optimizing biometric applications within smart infrastructure.
By eliminating passwords and PINs, biometric authentication provides a disruptive step in the field of cybersecurity and alleviates concerns around the security of copious amounts of data needed in a hyper-connected ecosystem.
While designing IoT applications for smart cities, biometrics are the ideal solution to achieving personalization and privacy backed by seamless authentication, provided the machinery involved is treated with a pristine level of care and pressure testing.
Financial
Gold’s Rising Appeal in the UAE Amidst Global Economic Shifts

James Campion, Popular Investor at eToro said, “Gold’s rally could be just beginning as it is an asset well positioned for almost any eventuality. It provides significant protection to a US Federal Reserve policy error, and hedges if inflation rises, and performs well if rates fall in the coming months.
“In the current global climate of heightened geopolitical risks, gold is not just a safe haven but a strategic asset. With central banks, including those in the Middle East, led by Qatar and Turkey, increasing their gold reserves significantly above average in the last two years, it is clear there is a concerted shift towards the asset.
“The dynamic of the gold market in Dubai reflects a broader trend where investors are increasingly looking to diversify their portfolios. The majority of investors remain historically underweight in gold, holding less than 1% of their portfolios in the metal, against a traditional recommendation of 5%. This trend comes at a time when the market volatility index (VIX) is hovering around a four-year low, suggesting a period of market complacency that could lead to increased volatility and further drive investors towards gold.
“Given the increased accessibility through online platforms to the GLD ETF and the ongoing economic indicators, we foresee a continued rise in gold investment globally and for some time, this could be the beginning of a gold super cycle.”
News
ServiceNow acquires Raytion to enhance GenAI-powered search and knowledge management capabilities on the Now Platform

ServiceNow has announced it has acquired Raytion to enhance GenAI‑powered search and knowledge management capabilities on the Now Platform. Raytion’s industry‑leading information retrieval technology will enable unified real‑time access to business‑critical data across multiple enterprise sources for a more powerful, efficient, and personalized AI search experience, all on a single technology platform.
The complexity of modern enterprise environments will drive the need for more intelligence about the data, so that organizations can take control of highly distributed, diverse, and dynamic information. With Raytion technology combined with ServiceNow AI Search, users can find the answers they require without having to know exactly where the information is located. Raytion’s technology will integrate secure access to information from enterprise data sources and allow ServiceNow’s AI Search to provide users with an industry‑leading, intelligent search experience and the information they need, all from a single-entry point. This includes data within ServiceNow and from third‑party systems.
“ServiceNow is accelerating work, uniting fragmented data into a single, intelligent platform that helps customers access and share knowledge across their organizations,” said Jon Sigler, senior vice president, Platform and AI, at ServiceNow. “Raytion’s information retrieval technology will set us apart by making relevant data sources searchable so everyone—employees, customers, and agents—get the answers they need, when they need them.”
Raytion’s GenAI‑powered search and knowledge management capabilities allow for cross‑enterprise data integration, pulling from the full universe of enterprise knowledge that exists in various knowledge repositories, rather than a subset. When combined with the ServiceNow Now Assist GenAI experience, data moves beyond disparate information to now providing users with more comprehensive, relevant search results in one centralized location, helping boost self‑service and case deflection. ServiceNow’s single data model – which seamlessly integrates people, services, and systems to empower AI capabilities – takes this even further, enabling a more personalized experience for users, drawing on employee history like previous searches and interactions so results are more relevant and tailored to their unique needs.
“Enriching GenAI with the specific up‑to‑date information an employee has access to across all relevant data sources makes not only business processes smarter but the whole enterprise,” said Valentin Richter, founder and CEO of Raytion. “The combination of ServiceNow’s single platform with Raytion’s secure enterprise data integration technology gives businesses a competitive advantage, allowing employees to solve problems and take informed action faster. We’re bringing together business‑critical information with intelligent GenAI‑powered search and reliable data retrieval, all in one place.”
News
Proofpoint warns of ticket scams as phony Paris Olympic Games 2024 sites proliferate
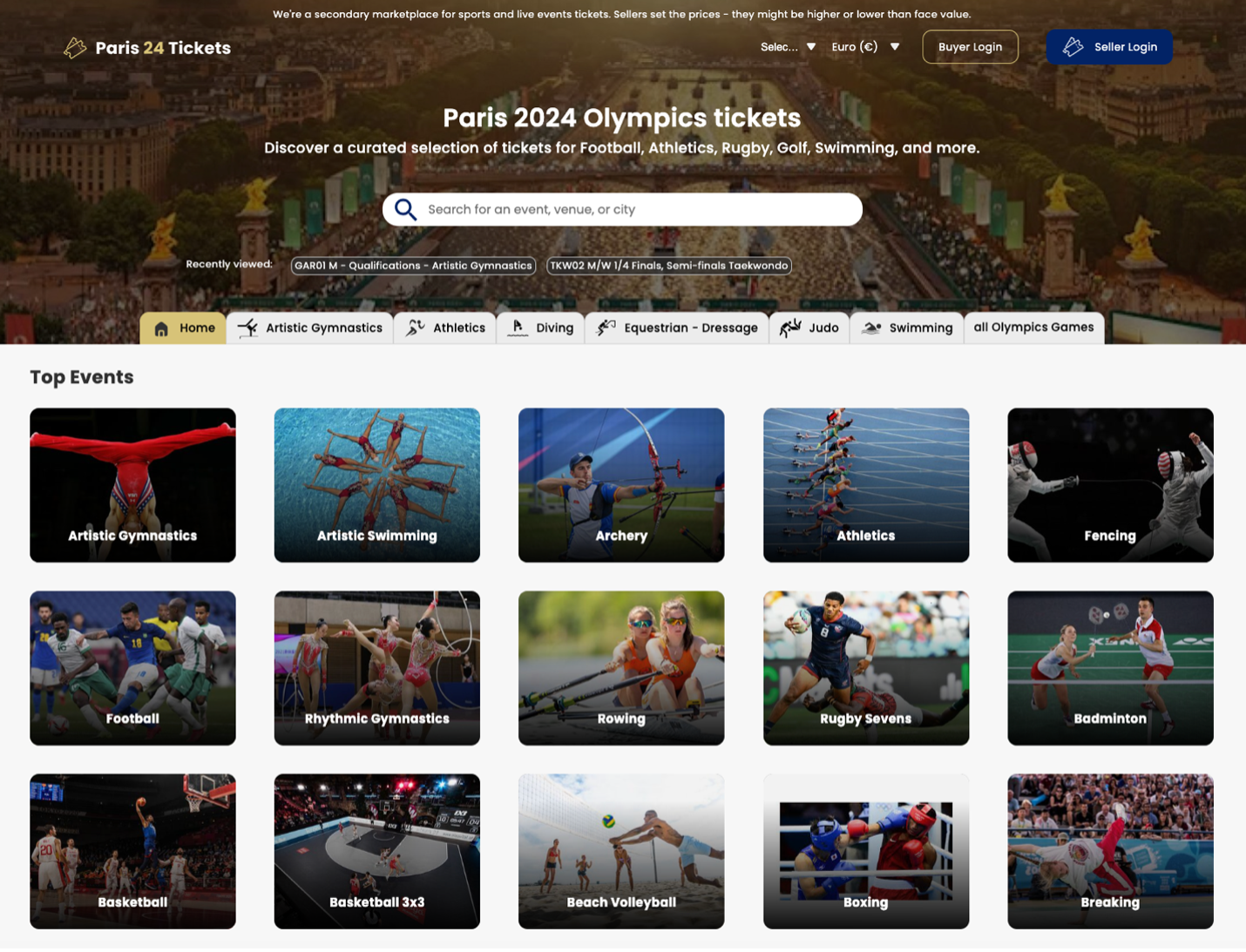
Leading cybersecurity provider Proofpoint recently identified a fraudulent website purporting to sell tickets to the Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games. The website “paris24tickets[.]com” claimed to be a “secondary marketplace for sports and live events tickets.” It was notably listed as the second sponsored search result on Google, after the official website, when searching for “Paris 2024 tickets” and related searches. Proofpoint confirmed with official sources in France that the site was fraudulent. Proofpoint’s Takedown Team worked with the registrar to suspend the domain quickly after its initial discovery.
Emile Abou Saleh, Senior Regional Director, Middle East, Turkey, and Africa at Proofpoint, said: “The buzz around mega-events like the Paris Olympics creates a feeding frenzy for cybercriminals. They exploit this excitement with social engineering – a sophisticated psychological manipulation tactic – effectively playing people, not technology. These same tactics fuel Business Email Compromise attacks, where they steal credentials, data, and money. Proofpoint’s 2024 State of the Phish report reveals a staggering 19% increase in BEC attacks last year. For fans in the Middle East, where social engineering is a dominant cybercrime weapon, remember to be vigilant and only trust verified sources. Don’t let your Olympic dreams turn into a security nightmare.”
The site that Proofpoint’s Takedown Team got suspended was sadly just one of many. According to the French Gendarmerie Nationale, their efforts in collaboration with Olympics partners have identified 338 fraudulent Olympics ticketing websites. Of these, 51 have been shut down, with 140 receiving formal notices from law enforcement.
On the website identified by Proofpoint researchers, the homepage listed many Olympic events, and if the user clicked on one of the sports icons, they were taken to a ticketing page that allowed the user to select tickets and provide payment data. The site also appeared to allow users to establish accounts to buy and sell tickets.
The website design appeared similar to other well-known ticketing sites visitors would be familiar with, increasing the site’s perceived legitimacy.
It is likely the threat actors managing this website were trying to steal money from people attempting to buy or sell Olympics tickets. It’s possible the site also collected personal information from people attempting to purchase tickets including names, contact information like email and mailing addresses and phone numbers, and credit card details.
The domain is believed to have been primarily distributed via ads in search results. While not observed in widespread email campaigns, the domain was observed in a small number of emails. In some cases, the bad actor sent emails claiming to provide “discounts” on tickets possibly of interest to the recipient. While researchers cannot confirm how the actor obtained the targets’ emails, it is possible the users included their email addresses when they signed up to the website or attempted to purchase tickets.
Fraudsters will always capitalize on current events, and the Olympic Games is no exception. Unsuspecting users likely clicked on the website because it appeared to be a legitimate entity that specialized in the sale of Olympic tickets. The website’s placement on the search engine under the official Paris Olympics ticket site could have further added to its legitimacy, convincing users that they were an authorized and safe source. While this specific domain should no longer be active, we expect other bad actors to take advantage of the event and create new fraudulent Olympics-related websites.
-

 Tech Interviews4 months ago
Tech Interviews4 months agoNavigating the Cybersecurity Landscape in Hybrid Work Environments
-

 Features2 months ago
Features2 months agoSecurity in the Cloud Age: Combating Risks with Hybrid Cloud Solutions
-

 Tech Features6 months ago
Tech Features6 months agoHow Telecommunications Providers Can Best Tackle DDoS Attacks
-

 Tech Features1 month ago
Tech Features1 month agoThe Middle East to Lead with Next-generation Mission Critical Communication Advancement
-

 Automotive5 months ago
Automotive5 months agoAl-Futtaim Automotive Builds On 23-Year Legacy of Trust & Leadership in UAE’s Pre-Owned Car Market to Sell Over 25,000 Used Vehicles in 2023
-

 Tech News7 months ago
Tech News7 months agoSenet enters MENA’s Competitive Gaming Scene with ‘skill-to-earn’ Platform
-

 Tech News4 months ago
Tech News4 months agoBrighton College Abu Dhabi and Brighton College Al Ain Donate 954 IT Devices in Support of ‘Donate Your Own Device’ Campaign
-

 Tech News6 months ago
Tech News6 months agoGoogle Appoints Ziad Jammal as Google Cloud Country Manager in the United Arab Emirates











