Financial
Empowering Entrepreneurs and Fostering Financial Wellness for a Thriving Future in the Region!

Integrator had an exclusive interview with Jigar Sagar, a UAE-based serial entrepreneur. In this conversation, he shares motivational, strategic, and actionable insights tailored for aspiring entrepreneurs, business professionals, and those passionate about finance and innovation.
Jigar, tell us the story of your beginnings and what is your core area of expertise?
My entrepreneurial journey began quite early, at age 10, working in my family’s retail shop in Sharjah’s Gold Souk. This early exposure was instrumental in shaping my understanding of business fundamentals. The dynamic nature of the gold market, with its constant price fluctuations, naturally drew me toward understanding numbers and financial mechanics. Every day after school, from 6 PM onwards, I would immerse myself in the family business, learning invaluable lessons about customer service, inventory management, and the importance of building lasting relationships with clients.
What started as basic bookkeeping in the family business evolved into a deeper passion for finance and accounting. The gold market taught me early on that success in business isn’t just about sales – it’s about understanding the numbers behind those sales, managing inventory effectively, and maintaining precise financial records. This realization led me to pursue a bachelor’s degree in business administration with a specialization in finance from the American University of Dubai, where I graduated with Cum Laude honors.
My core expertise lies in understanding the intricate relationship between numbers and business success. Whether it’s corporate finance, strategic planning, or risk management, I believe that financial literacy is the backbone of any successful enterprise. This financial acumen, combined with my practical experience in business setup and growth strategies, has been crucial in my journey from the Gold Souk to managing multiple successful ventures. My expertise has evolved to encompass not just financial management, but also strategic business development, risk mitigation, and the creation of sustainable business models that can weather market fluctuations and economic challenges.
Tell us about what inspired you to transition from a finance manager to an entrepreneur?
Entrepreneurship was always the end goal for me—employment was a stepping stone in my larger journey. My brief stint at HSBC’s treasury department and subsequent role as Finance Manager at Creative Zone helped me build a strong foundation for my entrepreneurial aspirations.
Employment served multiple crucial purposes: it allowed me to accumulate capital for future investments, provided hands-on experience in corporate operations, and offered valuable insights into both effective and ineffective business practices. I specifically chose to work at Creative Zone, a startup at the time, rather than working with a large multinational, because I recognised that startups offer accelerated learning opportunities and growth potential that established corporations typically can’t match.
In a startup environment, roles are often fluid, and this allowed me to gain experience across multiple aspects of the business. I progressively moved from finance to sales, then to operations, and eventually became the key point person for government relations. This comprehensive exposure was invaluable in understanding how different business components interact and influence each other.
What truly inspired me was the opportunity to build something from the ground up. At Creative Zone, I witnessed firsthand how good business relationships could lead to new venture opportunities. This experience culminated in my acquisition of a minority stake in the company pre-Covid, marking my first significant step from employee to owner.
The transition wasn’t just about changing roles – it was about fulfilling a vision I’d had since my early days in the Gold Souk. I wanted to create not just successful businesses, but entire ecosystems that could support and nurture other entrepreneurs. This desire led me to launch multiple ventures, each addressing specific market gaps and needs I’d identified during my employment years.
How did you approach financial management and scaling Creative Zone to become Dubai’s largest business setup advisory firm? Can you share the (financial) details of your exit from Creative Zone?
The scaling of Creative Zone was built on three fundamental principles I learned from my early days in the Gold Souk: meticulous financial management, customer service excellence, and continuous innovation in service offerings.
In the initial phases, our focus was primarily on robust cash flow management and maintaining lean operations. This meant being extremely mindful of our expenses while simultaneously investing in growth opportunities. Drawing from my family business experience, I understood that customer service would be our key differentiator in a competitive market.
We consistently expanded our service portfolio to address evolving market needs. This included launching Creative Zone Business Hub and Creative Zone Tax & Accounting, which helped create additional revenue streams while providing more comprehensive solutions to our clients. Our approach to growth was always customer-centric, ensuring that each new service offering addressed a genuine market need.
The success of this strategy culminated in a multi-million dollar exit to a fund. This exit validated our business model and growth strategy, while also providing resources for future ventures and investments in the UAE’s entrepreneurial ecosystem.
You had mentioned that hardworking people are paid the least during the Gladiator Summit in Dubai? What made you say so?
This observation comes from years of experience and studying successful business patterns. While our traditional education system promotes the idea that hard work alone equals success and higher compensation, the reality of modern business presents a different truth.
Don’t misunderstand – hard work is absolutely essential and non-negotiable for success. However, it’s the combination of hard work with smart strategic thinking that truly creates exponential value. I’ve seen countless examples of people who work incredibly hard in their jobs, putting in long hours and maximum effort, yet they remain in the same financial position year after year.
The key differentiator lies in how you channel that hard work. Are you building something sustainable? Are you creating systems that can work for you? Are you developing multiple revenue streams? These are the questions that separate those who are merely working hard from those who are creating lasting wealth.
When I started at the Gold Souk, I could have simply focused on being the hardest working person in the shop. Instead, I used that experience to learn about business operations, customer service, and financial management. I then applied these lessons to build multiple businesses, creating sustainable systems rather than just trading time for money.
The most successful entrepreneurs I’ve encountered are indeed hardworking, but they combine this with strategic thinking, market awareness, and the ability to build scalable systems. They outwork their competition while simultaneously working smart – creating businesses that can grow beyond their personal time investment.
Tell us in what ways are free zones adapting to the needs of today’s entrepreneurs, and what innovations are you bringing to these spaces?
The evolution of free zones in the UAE represents one of the most dynamic shifts in our business ecosystem. Today’s entrepreneurs demand more than just a business license—they need a comprehensive support system that enables their success, and free zones are rapidly adapting to meet these changing needs.
The primary transformation we’re seeing is the shift from traditional licensing centers to integrated business enablement hubs. Free zones are now focusing on making the entire process simpler, faster, and more cost-effective for entrepreneurs. This includes digitising operations, streamlining procedures, and reducing documentation requirements. What used to take weeks can now often be accomplished in days or even hours.
However, real innovation lies in how we’re reimagining the role of free zones in the entrepreneurial journey. Instead of being mere service providers, we’re transitioning these spaces into comprehensive market platforms. This means creating entire ecosystems where entrepreneurs can not only establish their businesses but also find partners, connect with customers, and access various support services.
Through my involvement with various free zones, I’ve focused on introducing innovations that address real entrepreneurial pain points. This includes developing new partnerships that provide value-added services.
You’ve mentioned a goal to empower over 100 million entrepreneurs globally. What drives this ambitious vision?
I believe empowering entrepreneurs is one of the most effective ways to build a better world. While individual inventions can certainly make an impact, entrepreneurs create lasting change by building sustainable businesses that serve society’s needs. They’re not just creating wealth, they’re solving problems, generating employment, and driving innovation across all sectors.
The goal of 100 million entrepreneurs might sound ambitious, but consider the ripple effect. If each entrepreneur creates even just a few jobs and serves a few hundred customers, we’re talking about improving millions of lives. These entrepreneurs will build businesses that not only serve today’s needs but anticipate and solve tomorrow’s challenges.
What really drives me is the long-term impact. When we empower entrepreneurs, we’re not just helping individuals succeed—we’re creating a chain reaction of positive change that will benefit future generations. These entrepreneurs will create the jobs of tomorrow, develop solutions for emerging challenges, and build the foundations for continued economic growth.
This is particularly relevant in the UAE, where we’re transitioning from attracting global wealth to nurturing homegrown innovation. By empowering entrepreneurs here and globally, we’re helping create a more dynamic, resilient, and prosperous world for future generations. It’s about building a legacy of sustainable growth and innovation that extends far beyond our own time.
Financial
RISK, RESILIENCE AND A 96 PERCENT: WHAT ACCA’S TOUGHEST PAPER TAUGHT ME ABOUT STRATEGY

Preeti Peter, student – BCom ACCA – MAHE Dubai
Advanced Financial Management is a paper that separates theoretical knowledge from applied thinking. It tests your ability to make strategic decisions under uncertainty, weighs competing risks in real time, and defends your reasoning when there is not one right answer. The pass rates reflect that difficulty. When I sat for the exam, World Rank 1 was never the target, surviving the paper with credibility was. I scored 96 out of 100. But the number, on its own, tells you very little. What matters is what the journey demanded: a complete rewiring of how I approached preparation, pressure, and failure.
Treating preparation like a financial model
Early on, I made a decision that changed everything: I would stop following a generic study plan. Instead, I approached my preparation the way an analyst might approach a sensitivity analysis. I tested variables by studying at different times of the day, experimenting with visual mapping versus deep reading. Each iteration helped me identify what produced the best results for my learning style.
This was about precision, not volume. In finance, we talk about capital allocation, where you deploy resources matters more than the sheer amount available. I applied the same logic to my time. High-yield areas got the most attention. Weak spots got targeted effort. Comfortable topics got less.
Strategy is not a luxury reserved for boardrooms. It belongs in every decision you make.
The negative cash flow phase
There is a phase in every long-term project, financial or otherwise, where the output does not match the input. In corporate finance, we call this negative cash flow. You are investing, and the returns have not materialised yet.
My first few weeks of AFM preparation felt exactly like that. I was putting in the hours, but comprehension was patchy. It would have been easy to panic or abandon ship for a different approach.
Instead, I recognised the phase for what it was: temporary. Every business that reaches breakeven has survived this stage first. I leaned into discomfort, trusted the process, and kept showing up. Slowly, the fog lifted.
That early patience was critical. If I had changed course every time results lagged behind effort, I would never have built the understanding that carried me through the exam.
Discipline over motivation
There is a popular idea that success comes from being motivated. I found the opposite to be true. Motivation is unreliable, it fluctuates with your mood, your energy, a difficult question that throws you off balance.
What carried me was routine. I built a daily structure that operated regardless of how I felt on any given morning. Good days and bad days received the same treatment: sit down, open the material, work through the plan.
During my time at Manipal Academy of Higher Education Dubai, I learned to value consistency over intensity. Resilience, I realised, is not about gritting your teeth and pushing through pain. It is about designing a process robust enough to function even when you are running on empty.
Confronting discomfort deliberately
One of the more counterintuitive lessons AFM taught me was about comfort zones. When preparing for a high-stakes exam, there is a strong temptation to practise what you already understand. You move through questions quickly, confidence builds, and the work feels rewarding.
But that feeling is misleading. The topics I avoided, the ones that made me uneasy, the questions I got wrong repeatedly were precisely where the growth was. I started restructuring my study sessions to front-load the most difficult material. If a topic made me uncomfortable, it went to the top of the list.
Over time, those uncomfortable sessions became the foundation of my exam performance. The questions that would have caught me off guard were the ones I was most prepared for.
Managing pressure, not just content
I remember finishing a mock exam and feeling genuinely defeated. The time pressure had overwhelmed me. I knew the material but knowing the material and performing under timed conditions are two very different skills.
That experience changed my approach. I began treating exam technique as its own discipline, separate from subject knowledge. I practised under strict time limits and developed a method for approaching unfamiliar questions: pause, outline, then write.
On exam day, there were moments where questions looked unfamiliar at first glance. Instead of panicking, I paused, outlined a structure, and worked through each part methodically. I finished on time, with every question addressed.
The real lesson: stress does not disappear because you have prepared well. You simply get better at functioning within it.
Feedback as fuel
A score of 96 percent might suggest a clean, linear path to the top. The reality was messier. Mock results were humbling. Feedback on practice answers was sometimes blunt.
But I made a conscious decision early on, I would treat every piece of critical feedback as information, not as judgement. If a mock answer missed the mark, I wanted to understand why so, to close the gap between where I was and where I needed to be.
That openness to correction was, I believe, one of the most important factors in my result. The students who improve fastest are rarely the most talented. They are the ones willing to be told they are wrong and to adjust accordingly.
Beyond the exam
World Rank 1 was a rewarding outcome. But the rank is a snapshot, a single data point from a single day.
Structured thinking. Disciplined preparation. The ability to remain calm when the stakes are high. A willingness to sit with discomfort rather than avoid it. These are not exam skills. They are life skills.
AFM taught me that risk is not something to fear. It is something to understand, to price, and to manage. That principle holds whether you are valuing a derivative or deciding how to spend your next hour. The same applies to every challenge worth pursuing.
Financial
Abu Dhabi-Based Asif Aziz Will Illuminate London’s West End with Ramadan Lights for Fourth Year, Expanding Global Cultural Impact
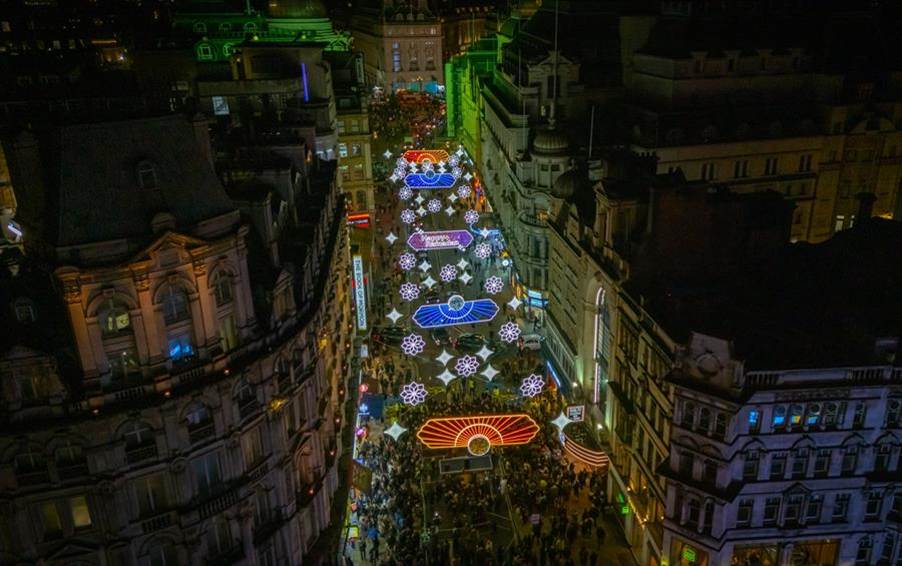


Abu Dhabi–based businessman and philanthropist Asif Aziz, Founder of Criterion Capital, continues to set the benchmark for large-scale public programming as his landmark Ramadan Lights London initiative returns for a spectacular fourth edition.
Having launched Western Europe’s first-ever aerial Ramadan lights in 2023, Aziz has permanently reshaped the cultural landscape of London. What began as a groundbreaking concept has since evolved into a globally-recognised, free, annual celebration delivered for civic good, placing the values of Ramadan at the heart of one of the world’s most influential cities.
Delivered through Aziz’s charity, The Aziz Foundation (Registered Charity: 1169558), Ramadan Lights London demonstrates values-led leadership at scale, showing how faith, culture and community can intersect to create lasting social impact.

At the heart of the programme is the flagship aerial lights display along Coventry Street: a pioneering installation of more than 30,000 sustainable LED lights arranged in intricate geometric patterns inspired by Islamic art, with motifs representing suhoor and iftar.
The 2026 programme will open with a high-profile switch-on ceremony, with the lights activated by Sir Sadiq Khan, Mayor of London, Rahima Aziz BEM, Trustee at The Aziz Foundation, and Adil Ray OBE, actor and broadcaster, in the presence of senior public leaders, distinguished cultural figures, ambassadors and international dignitaries. The display will remain illuminated until 18th March 2026, before transitioning to Eid Lights through to 24th March 2026.

A selection of artworks featured in Shared Light – central London’s first interfaith art exhibition. Left: Rooh-e-Bhag (Soul of the Garden) (2025) by Mohamad Aaqib Anvarmia. Centre: Hospitality of Abraham – After Rublev (2025) by Meg Wroe. Right: Mettavihari (2025) by Colin Panrucker
This year will also see the launch of Shared Light – central London’s first interfaith Ramadan art exhibition – bringing together artists of all faiths and backgrounds whose work is inspired by the values of Ramadan. The exhibition will be unveiled by the Deputy Lord Mayor of Westminster and hosted at Aziz’s Zedwell hotel at Piccadilly Circus, reinforcing culture’s role as a bridge between communities in one of the world’s most iconic city centres.

Ramadan Lights London will also welcome back Ramadan Delights, London’s first curated iftar food trail, introduced by Aziz in 2025 and now firmly established as a district-wide West End experience. The trail brings together leading international brands and heritage institutions – including Fortnum & Mason, 1 Leicester Square Rooftop, PizzaExpress and Shake Shack- offering special menus, exclusive offers and halal-friendly dining while supporting local businesses and the economic vitality of the area.
This year, the initiative is further strengthened through a partnership with Centrepoint, the UK’s leading youth homelessness charity, reflecting a shared commitment to social mobility, economic empowerment and supporting disadvantaged young people.
Commenting on the programme, Asif Aziz said: “Ramadan Lights London reflects how the values of Ramadan – generosity, reflection and empathy – can contribute meaningfully to civic life. It is about thoughtful engagement and creating shared experiences that strengthen communities and endure over time.”
Beyond Ramadan Lights London, Aziz’s wider philanthropic work continues to deliver impact. Since 2015, The Aziz Foundation has awarded over 750 scholarships, supported more than 100 media internships, and delivered extensive mentorship programmes across key industries. Aziz is also leading the regeneration of Criterion Capital’s Grade II-listed London Trocadero, transforming the landmark into a 1,000-capacity mosque and community centre – a long-term investment in cultural and faith infrastructure in a major global city.
Alongside his charitable endeavours, Aziz is establishing a scalable, world-class co-investment platform in Abu Dhabi, working with UAE institutions to deploy capital into transformative urban and living-sector opportunities across Europe and the Middle East, with a continued focus on sustainable social outcomes.
Financial
ENOVATE AND COBI LAUNCH LARGE-SCALE AI-POWERED DIGITAL PAYMENT INFRASTRUCTURE

eNovate, a subsidiary of eFinance Investment Group, and Cobi, a UAE-headquartered AI-native customer intelligence platform, today announced the integration of Cobi’s AI-powered intelligence infrastructure across its digital payment ecosystem to redefine how young people across Egypt engage with digital financial services. Enabled through Mastercard’s Engage programme, the partnership combines eNovate’s digital payments product suite and Cobi’s AI-powered engagement platform to give financial institutions a new level of intelligence, personalisation, and behavioural insight across their customer base. As the MENA region emerged as a global hub for financial services innovation in 2025, fuelled by government initiatives and rapid digital payments growth, the focus is shifting toward AI-powered engagement and intelligence at scale.
The collaboration begins with the Rize app, eNovate’s flagship digital wallet, where Cobi’s intelligence layer will power real-time personalisation for Egypt’s youth segment. With 85% of people across MENA already using at least one emerging payment method, this allows banks and fintechs to better understand spending behaviours, identify friction, and deliver timely product interventions that drive activation, loyalty, and long-term customer value. The capability will extend across eNovate’s broader digital payment services, forming Egypt’s first large-scale AI-driven portfolio management infrastructure.
With the MENA region’s AI in financial services market projected to reach $4.7 billion by 2032, underscoring the scale of opportunity for intelligent, data-driven payment infrastructure across the region. At the core of the partnership is Cobi’s behavioural AI engine, which builds deep context on how users engage, identifies patterns, and recommends or triggers next-best-actions across acquisition, activation, and retention journeys for customers combining it with eNovate’s role as a central payments and digital services provider to Egypt’s banks, telcos, fintechs, merchants, and government-linked entities, the collaboration marks a major step toward intelligent, personalised financial experiences across the country.
Nashwa Kamel, CEO of eNovate, explained: “eNovate is committed to enabling banks & financial institutions with modern, data-driven capabilities. Partnering with Cobi allows us to introduce real-time intelligence into every digital wallet and payment experience we support, starting with the youth-focused Rize app. This collaboration strengthens our mission to provide Egypt with the most advanced and responsive payment infrastructure that provides insights into spend behaviour, helping banks & financial institutions to spot inefficiencies, optimize costs, and make smarter, data-driven decisions. By turning raw spend data into strategic intelligence, businesses can anticipate trends, strengthen supplier relationships, and accelerate sustainable growth.
Darren Edmund, CEO of Cobi, highlighted: “Our partnership with eNovate represents a fundamental shift in how digital payment infrastructure operates. By embedding Cobi as the intelligence layer across eNovate’s ecosystem, we are enabling banks and financial platforms to move beyond static transaction processing toward real-time, adaptive systems that understand and respond to user behaviour instantly. This allows institutions to personalise at scale, optimise portfolio performance, and build deeper, longer-lasting customer relationships. We’re glad to have had Mastercard’s Engage programme support this collaboration.”
Looking ahead, the partnership will extend toward agentic payment experiences, where AI not only analyses user behaviour but autonomously recommends or initiates actions that improve financial outcomes, ushering in a new era of intelligent and proactive financial services across Egypt. The initial deployment begins in Q1 2026, with expansion planned across additional eNovate-powered platforms and regional markets.
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoDenodo Bolsters Executive Team by Hiring Christophe Culine as its Chief Revenue Officer
-
News10 years ago
SENDQUICK (TALARIAX) INTRODUCES SQOOPE – THE BREAKTHROUGH IN MOBILE MESSAGING
-

 VAR11 months ago
VAR11 months agoMicrosoft Launches New Surface Copilot+ PCs for Business
-

 Tech Interviews2 years ago
Tech Interviews2 years agoNavigating the Cybersecurity Landscape in Hybrid Work Environments
-

 Tech News8 months ago
Tech News8 months agoNothing Launches flagship Nothing Phone (3) and Headphone (1) in theme with the Iconic Museum of the Future in Dubai
-

 Automotive1 year ago
Automotive1 year agoAGMC Launches the RIDDARA RD6 High Performance Fully Electric 4×4 Pickup
-

 VAR2 years ago
VAR2 years agoSamsung Galaxy Z Fold6 vs Google Pixel 9 Pro Fold: Clash Of The Folding Phenoms
-

 Tech News2 years ago
Tech News2 years agoBrighton College Abu Dhabi and Brighton College Al Ain Donate 954 IT Devices in Support of ‘Donate Your Own Device’ Campaign